Why Semantic SEO is the Only SEO for the AI Age
Old SEO tricks aren’t cutting it anymore. Google, powered by advanced AI like Gemini and its AI Overviews (formerly SGE), now understands not just the words you type, but the entities, concepts, and true intent behind them. That’s why simply stuffing pages with exact-match keywords won’t get you far.
If you want to rank in 2025, you need a strategy that matches how search engines and generative AI think. That’s where Semantic SEO comes in. It’s about building content that answers every possible question your audience might have, while speaking the same “language” of context and meaning that Google’s AI understands.
In this guide, you’ll learn how Semantic SEO works, why it’s the future of search, and exactly how to use it to boost your rankings and secure visibility in the new AI-driven SERP landscape.
We’ll break it down into practical steps, real examples, and the best tools to get you started.
| Quick Summary |
| Semantic SEO focuses on topics, entities, and user intent instead of just exact-match keywords. By organizing content into topic clusters, using related terms and named entities, and implementing robust schema markup, you help Google and its AI Overviews understand your site’s complete topical context, not just its words. This boosts rankings for a wider range of searches, improves relevance, establishes topical authority, and is the key to winning visibility in AI-generated summaries. |
What is Semantic SEO and How Does It Work?
In the past, SEO was mostly about using as many keywords as possible (often called keyword density). But now, with Semantic SEO, it’s more about understanding what people are truly looking for—their core problem or need—and providing a comprehensive solution.
Semantic SEO is the practice of creating content for a topic or entity instead of a single keyword.
Semantic SEO begins with understanding the entity—the real-world person, place, or thing—that your content relates to, moving search beyond simple keyword matching.
It means you must consider the search intent (Informational, Commercial, Navigational, Transactional) and provide the user with all the related, in-depth information they need to satisfy that intent.
The Scenario Before Semantic SEO
A few years back, repeating a keyword like “Semantic SEO” multiple times could rank your blog for only that specific term.
The Scenario With Semantic SEO in 2025
Today, a single, high-quality article optimized for Semantic SEO will not only answer the primary search query but also preemptively answer all the related, follow-up questions a user may have.
For example, if you search for “Semantic SEO,” a good article should immediately address:
- What Semantic SEO is (Definition).
- Why it matters for 2025 (Benefits).
- How to implement it (Strategy and Tools).
- The connection to Google’s AI (SGE), E-E-A-T, and Entities.
A good Semantic SEO-optimized article covers all content angles (subtopics, entities, and intents) behind a core search query, building Topical Authority for your entire domain.
Why is Semantic SEO Non-Negotiable for 2025?
Semantic SEO allows the creation of content with a bigger purpose: to be the most valuable, authoritative resource on a given topic. This directly aligns with Google’s core ranking philosophies.
Benefits of Practicing Semantic SEO
- Your Content Ranks Higher for Broader QueriesBy reflecting the comprehensive topic model Google has built, your content is seen as the authoritative source, leading to better rankings across a wider family of related searches.
- You Rank for More Keywords (The Long-Tail Advantage)When you write content around an entire topic, you naturally incorporate dozens of related terms, long-tail phrases, and specific questions (semantic keywords/entities). This means your single content piece will rank for hundreds of search queries, not just one.
- You Win Visibility in AI Overviews and Rich Results (Generative Engine Optimization – GEO)Semantic structure (headings, lists, schema) and topical depth make your content easy for AI models to parse, extract, and use for their generated summaries. This is the key to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), leading to inclusion in AI Overviews (the new featured snippet) and other high-value SERP features like PAA.
- You Establish Your Authority (E-E-A-T)Writing topic-focused, detailed, and accurate content sends powerful E-E-A-T signals to Google. Your website is seen as having topical authority, making it easier to rank new content on related subjects. Note: E-A-T was updated to E-E-A-T to emphasize Experience—showcasing real-world use or testing is now crucial.
- Your Visitors Stay on Your Website LongerComprehensive content that fully covers a topic satisfies user intent in a single visit, increasing dwell time and lowering your bounce rate. This is a strong user experience signal that helps your content rank higher.
How Semantic SEO Came into Existence
The evolution of search is a journey from simple keyword matching to complex contextual understanding. This journey was primarily driven by major Google algorithm updates.
| Google Algorithm Updates that Built Semantic Search |
| I. Hummingbird (2013): The true beginning of Semantic Search. It moved Google from matching words to matching meaning and intent using Natural Language Processing (NLP). |
| II. RankBrain (2015): The first machine-learning AI component integrated into the ranking system. It learns how to interpret new, ambiguous, or conversational search queries by looking for similarities between them and successful, highly relevant pages. |
| III. BERT (2019): Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. This was a massive leap forward in NLP, allowing Google to understand the context of every word in a sentence, drastically improving its ability to interpret complex, conversational, and long-tail queries. |
| IV. AI Overviews/Gemini (2024-2025): The culmination of all prior updates. AI Overviews directly apply semantic understanding to generate a summarized, cited answer, making Entity-Based SEO and Schema more important than ever to be recognized as a source. |
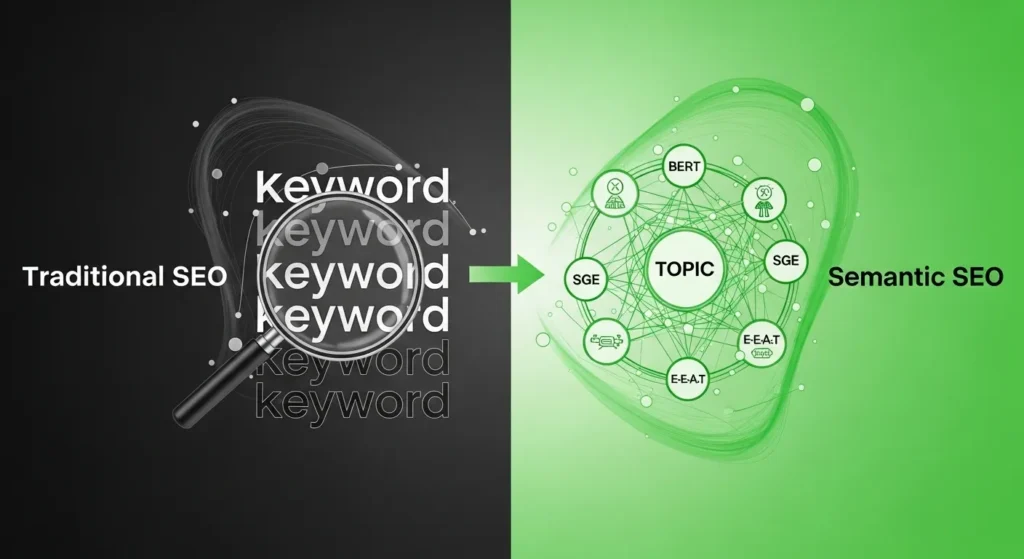
Semantic SEO vs. Traditional SEO: The 2025 Shift
The difference isn’t that keywords are dead; it’s that context is king.
| Semantic SEO (2025 Approach) | Traditional SEO (Legacy Approach) |
| Focus: Topics, Intent, and Entities | Focus: Exact-match Keywords and Density |
| Optimized to Meet: User intent (a complete solution) | Optimized to Meet: Search engine keyword targets |
| Content Strategy: Topic Clusters and Pillar Pages | Content Strategy: One page per keyword |
| Ranking Goal: Topical Authority and AI Visibility (GEO) | Ranking Goal: High rank for a single term |
| UX Focus: High dwell time, low bounce rate, all answers in one place. | UX Focus: Secondary to keyword placement. |
Semantic SEO bridges the gap between your content and the user’s ultimate intent, ensuring you’re seen as the most authoritative, trustworthy source.
7 Essential Semantic SEO Strategies for 2025
To thrive in the AI-driven search landscape, your content strategy needs to move from mere keyword research to full-topic orchestration.
1. Master Search Intent and User Journey Mapping
The most critical step is understanding the intent behind the search query. Google wants to offer a complete user journey.
- Actionable Tip: Anticipate the searcher’s next three questions after they get the primary answer. For the query “how to use WordPress,” they might also need: “Best plugins for beginners,” “How much does WordPress cost,” and “How to choose a theme.” Address all these in-depth sections.
2. Focus on Entity-Based Content Creation
In 2025, Google recognizes named Entities (people, places, organizations, concepts like “Semantic SEO,” “BERT,” or “Google”) and the relationships between them via its Knowledge Graph.
- Actionable Tip: Identify the core entities in your topic. Ensure you mention, define, and connect these entities correctly. Use tools that check your content for entity coverage (e.g., Google’s Natural Language API, Clearscope, Surfer SEO). This is what signals true topical relevance to Google’s AI.
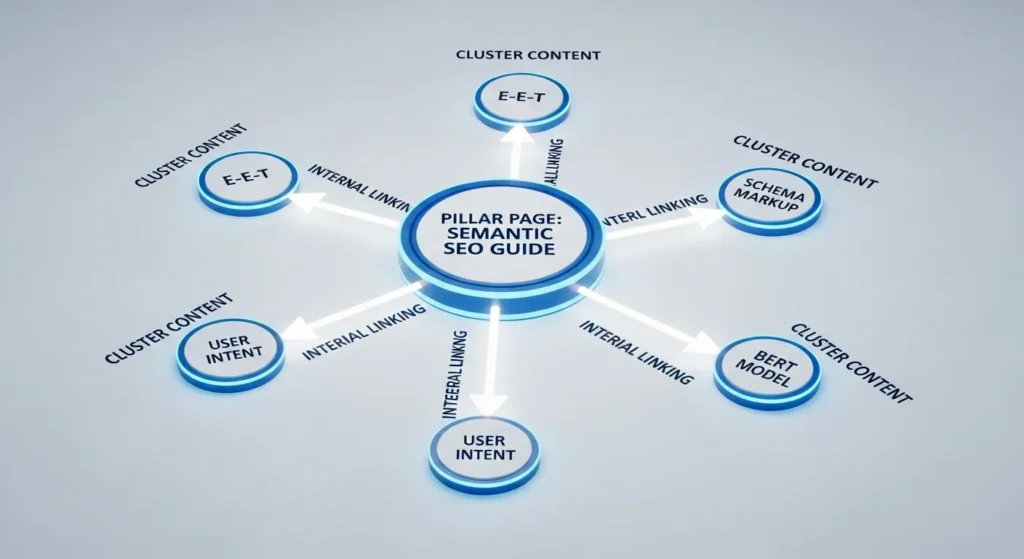
3. Implement Topic Clustering (Hub-and-Spoke Model)
A Topic Cluster is an interlinked group of pages revolving around a central concept. This structure is a direct signal of Topical Authority.
- Pillar Page (Hub): A broad, high-level guide covering the main topic (e.g., “The Ultimate Guide on Semantic SEO”).
- Cluster Content (Spokes): In-depth articles that explore subtopics mentioned in the pillar (e.g., “How BERT Impacts Semantic Keyword Research,” “Advanced Schema Markup for Entities”).
- Linking: All cluster pages must link back to the Pillar Page, and the Pillar Page must link out to all the cluster pages.
4. Optimize for Conversational and Long-Tail Queries
AI Overviews and the rise of Voice Search (which involves natural language) reward content that directly and concisely answers questions.
- Actionable Tip: Use the People Also Ask (PAA) and Related Searches sections as mandatory subheadings (H3s or H4s) in your content. Phrase your headings as direct questions (“What are Semantic Keywords?”) and follow immediately with a clear, concise answer (a citation-ready snippet), ideally in a list or short paragraph.
5. Leverage Advanced Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Schema is a language that explicitly tells search engines what your content means. For 2025, using schema is the most direct way to speak to Google’s AI.
- Actionable Tip: Go beyond basic
Articleschema. Use specific types likeFAQPagefor your PAA sections,HowTofor procedural content, and ensure you use thementionsproperty to explicitly identify the key entities on the page. Use a tool like WordLift (paid) or a dedicated WordPress plugin to correctly implement this.
6. Write Detailed, Comprehensive Content
While length alone isn’t a ranking factor, topical depth is. Comprehensive content naturally includes more entities and semantic keywords.
- Actionable Tip: Don’t just focus on word count. Use tools like AnswerThePublic or your favorite SEO content editor to find all the related questions, prepositions, and comparisons for your topic. If a top-ranking competitor is missing a key subtopic, own it and cover it better.
7. Prioritize Page Experience (Core Web Vitals)
Google confirmed that Core Web Vitals (CWV) are a component of the Page Experience signal, which is a ranking factor. Excellent UX and fast loading times are the foundational layer for your Semantic SEO efforts.
- Actionable Tip: Focus on the stable CWV metrics: LCP (Largest Contentful Paint < 2.5 seconds), INP (Interaction to Next Paint < 200 milliseconds), and CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift < 0.1). Semantic content is often long and media-rich, so aggressively optimize images and defer non-critical CSS/JS to maintain speed.
Top Semantic SEO Tools for 2025
No single tool is enough, but combining a few allows you to effectively implement the strategies above.
| Tool | Focus & How to Use It |
| Google Search Console | FREE. Essential for finding the long-tail queries (semantic keywords) your page already ranks for, and which subtopics to expand. It also monitors your Core Web Vitals. |
| Answer The Public | FREE/Paid. Excellent for quickly generating question-based and prepositional queries (“Semantic SEO for a startup,” “Semantic SEO vs keyword stuffing”) to use as subheadings and PAA answers. |
| Google Autocomplete & Related Searches | FREE. Your fastest source for discovering immediate LSI/semantic keywords and user intent signals. Use these suggestions as subtopic ideas. |
| Surfer SEO / Clearscope / Frase (Paid) | Paid (Recommended). These content optimization tools use AI/NLP to compare your content against the top-ranking pages, score your topical coverage, and suggest relevant entities/semantic keywords to include. |
| LLMrefs (Emerging GEO Tool) | Paid (Specialized). A new class of tool that specifically tracks if and how often your content is cited by Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT or Perplexity, helping you measure your Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) success. |
Semantic SEO: Your Shortcut to Long-Term Rankings
Search is evolving fast, and Google’s AI updates reward content that understands context, entities, and intent. That’s exactly what Semantic SEO delivers.
Start by mapping your topics, connecting related pages into clusters, and speaking your audience’s natural language (and Google’s AI language of entities). Add robust schema, prove your E-E-A-T, and keep refining.
The sooner you focus on meaning over strings, the sooner you’ll rank for more searches, attract higher-quality visitors, and future-proof your SEO against the next inevitable AI update.
Your competitors are already optimizing for meaning. It’s time you led the charge.
Ready to dive deeper into the AI side of things? Check out our guide on Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) to learn how to get your content cited by AI.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the biggest difference between Semantic SEO and traditional Keyword SEO in 2025?
Traditional Keyword SEO focused on optimizing a page for an exact-match keyword and its simple variations (e.g., repeating “best laptop 2025”).
Semantic SEO in 2025 focuses on meaning, context, and user intent by optimizing for entities (concepts, people, places, things) and their relationships. The goal is to comprehensively answer all related questions surrounding a topic, which is essential for ranking highly in the age of Google’s AI Overviews (SGE) and the Gemini model’s deep contextual understanding.
What is an Entity in Semantic SEO?
An Entity is a distinct, well-defined concept, object, person, or place that Google can recognize and track, like “Apple Inc.,” “Quantum Physics,” or “Eiffel Tower.”
Unlike a simple keyword, an entity has attributes and established relationships with other entities (stored in Google’s Knowledge Graph). Optimizing for entities means ensuring Google correctly recognizes your content’s main subject and its topical connections, which is the foundation of modern search ranking.
Are LSI Keywords the same as Entities or Semantic Keywords?
No. The concept of LSI Keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing) is an outdated SEO myth that Google has explicitly stated they do not use.
Modern search engines use advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) like BERT and MUM (now integrated into Gemini) to understand true Semantic Relationships between entities. The focus has entirely shifted from simple word co-occurrence (LSI) to deep, contextual topic comprehension (Entities). You should focus on entities and comprehensive topic coverage, not LSI.
How does E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) relate to Semantic SEO?
E-E-A-T is directly supported by Semantic SEO.
Semantic SEO helps Google understand what your content is about (through entities and topic clusters).
E-E-A-T helps Google determine who wrote it and why they should be trusted on that topic (through clear author bios, citations, external mentions, and depth of experience).
By establishing deep Topical Authority through Semantic SEO, you provide the structural evidence Google needs to validate your E-E-A-T credentials and prioritize your content, especially in YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics.
What is the role of Topic Clusters in Semantic SEO for 2025?
Topic clusters are the fundamental structure of a Semantic SEO strategy. They are a group of interlinked pages centered around a single, broad pillar topic.
This structure tells Google:
Topical Depth: That you cover a subject comprehensively.
Entity Relationships: How various sub-topics (entities) relate to the main idea.
This organization improves internal linking, user experience, and your overall domain authority, making your site a more reliable source for AI-driven search results.
Ensure your site structure and internal linking reinforce the relationships between your topic cluster content so search engines can easily crawl and index your entire knowledge base.
Do I still need to use Schema Markup if I am doing Semantic SEO?
Yes, absolutely. Schema Markup (specifically JSON-LD) acts as a translator, explicitly confirming to search engines and AI exactly which entities are on your page and what their attributes are (e.g., this person is the author, this is a Product, this is an Organization).
In 2025, using Organization Schema and Person Schema to define yourself as an entity and link to the same entity across platforms is crucial for solidifying your E-E-A-T and helping your content appear in Rich Results and AI Overviews.