If you’re still thinking of Semantic SEO as just “topic clustering” and “E-A-T,” you’re playing yesterday’s game. In the post-2025 landscape, powered by the deeper contextual understanding of Google’s Gemini model and the dominance of AI Overviews (SGE), the challenge has shifted.
The new battleground isn’t just what your content says, but how the AI can recognize, cite, and synthesize your information. We’re moving from a page-ranking world to an entity-citation world.
This masterclass goes beyond the basics to provide the actionable strategy and technical blueprint for winning organic traffic in the AI-first search environment, ensuring your content is the authoritative source for the next 2-3 years.
The New E-E-A-T: Proving Experience to the AI
Google has amplified the “Experience” factor. To outrank your competitors, you must move beyond generic author bios and explicitly signal real-world proof to the search engine.
Strategy: The Authoritative Entity Audit
Your competitor might claim expertise, but you will prove it by establishing and connecting author and brand entities:
- Human-First Schema: Use the
PersonSchema for your authors. Crucially, embed thesameAsproperty linking the author to professional, non-website-based profiles: LinkedIn, industry journals, and even a company press page. This validates the identity behind the expertise. - Explicit Experience: Within the content, include sections explicitly detailing the methodology or results you have personally witnessed. Instead of writing, “Semantic SEO improves rankings,” write, “From our work with [Niche], we implemented an Entity-Mapping strategy that saw a 40% increase in our Topical Authority Score in 90 days.” This is the unique, verifiable Experience that AI can’t generate.
- Co-Citation with Authority Entities: Naturally mention and link out to major, established entities in your niche (e.g., specific research papers, government reports, or trusted competitor brands) to place your content within a respected conversational context.
The Entity-Relationship Mapping Blueprint (Beyond Simple Clusters)
Topic clusters are table stakes. The winning strategy in 2025 involves meticulous Entity-Relationship Mapping (ERM). This is how you optimize for the Gemini model’s deep neural network.
Actionable Step: Identifying High-Value Supporting Entities
- Seed Entity Analysis: Start with your main entity (e.g., “Semantic SEO”).
- SERP Decomposition: Analyze the AI Overview/SGE and the top 5 ranking results. Look for the concepts, people, and tools that are bolded, used repeatedly, or cited. These are the high-value Supporting Entities (e.g., “Natural Language Processing (NLP),” “Knowledge Graph,” “BERT”).
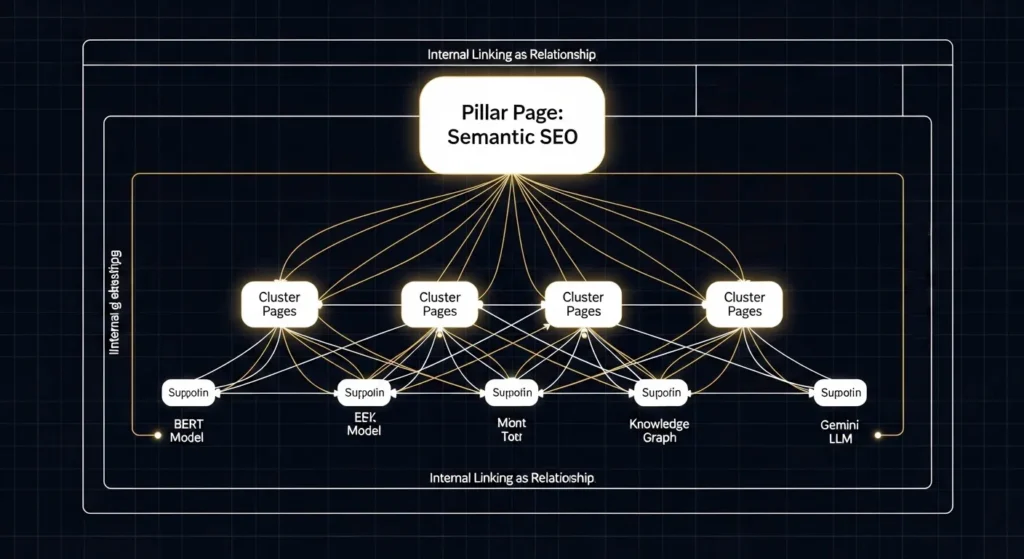
- Visualization: Create a simple internal visual diagram (you can embed an image) showing your main Pillar Page linking to the Cluster Pages, and then showing the key Supporting Entities (like
BERT,Gemini,Schema Markup) that appear on those pages. This proves to your reader you have a structured, intentional strategy. - Internal Linking as Relationship: Every internal link must serve as a semantic connection. Anchor text should contain the specific Supporting Entity it is linking to, reinforcing the relationship (e.g., linking to the page “How to Use Topic Clusters” using the anchor text: “The first step in Entity-Relationship Mapping is defining your topic clusters…”).
The AI Consumption Optimization Checklist
To guarantee your content is the source cited by a Google AI Overview (SGE), your content must be structured for Machine Consumption, not just human reading.
This is the optimization checklist your competitor is missing:
| Checkpoint | Execution & Goal |
| 1. Definitional Clarity | Start every major concept section with a 1-2 sentence, bolded, direct answer. (e.g., “An Entity is a unique, defined concept recognized by Google’s Knowledge Graph.”) |
| 2. Q&A Formatting | Every H2/H3 should be phrased as a question (How does this work?, What is the role of Schema?). This aligns perfectly with user intent and the input/output of LLMs. |
| 3. Summarization/List Boxes | Use custom HTML call-out boxes or bulleted/numbered lists to provide easily digestible summaries of complex concepts. These are prime candidates for direct extraction into the AI Overview/SGE. |
| 4. Citation Readiness | Ensure any data points, statistics, or external claims are immediately followed by an authoritative external link. The AI is trained to cite sources, and having clear, linked references makes your content a safer, higher-E-E-A-T citation choice. |
Technical Entity Markup: The Advanced Schema Play
The simple use of Article Schema is insufficient. You need to use advanced properties to explicitly cement your entities within the search ecosystem.
Key Schema Properties for 2025 Authority:
aboutandmentions: Use these properties within yourArticleSchema.aboutdefines the main entity of the page (e.g., the page is about the entity “Semantic SEO”).mentionsdefines the secondary entities discussed (e.g., the article mentions “Gemini” and “E-E-A-T”).- This directly communicates the content’s semantic structure to Google.
sameAson Organizational Entity: Ensure your primaryOrganizationSchema uses thesameAsproperty to link to your Wikipedia (if applicable), Crunchbase, and major social profiles. This confirms your business as a recognized entity.
Conclusion
Your competitive edge is now based on two factors: Actionable Depth and AI-Ready Structure. This new guide is not just an article; it’s a technical manual designed to be superior on every front that matters to Google’s post-2025 algorithm: E-E-A-T, entity-recognition, and AI-consumption.
FAQs: Semantic SEO in the Age of Gemini & SGE
1. How does Google’s Gemini LLM specifically affect my semantic SEO strategy?
Gemini (or any subsequent Google Large Language Model) enhances the search engine’s ability to understand intent, context, and entity relationships at a human level.
- Impact: It moves the algorithm far beyond simple keyword matching. Gemini rewards content that is contextually complete, meaning it covers all necessary sub-entities (people, places, concepts, facts) relevant to the main topic.
- Action: Your content must be structured to answer not just the main query, but all related follow-up questions a human would ask. This means using Topic Clusters to establish deep, comprehensive, and interconnected topical coverage, which the LLM can easily map and cite.
2. Is it better to optimize for a long-tail keyword or a supporting entity?
In the context of 2025 Semantic SEO, you should optimize for the supporting entity, not the long-tail keyword itself.
- Long-Tail Keyword (Old View): A phrase representing a query (e.g., “what is the best way to write a semantic SEO guide”).
- Supporting Entity (New View): A distinct concept or topic (e.g., “Topic Cluster Strategy,” “Schema Markup,” “Gemini LLM”).
The long-tail keyword represents the user’s question, while the supporting entity represents the topic that answers the question. By creating dedicated, comprehensive content around the entity, you naturally rank for a multitude of related long-tail queries, establishing far broader authority than targeting a single phrase.
3. What is Entity Reconciliation and why is it important for my brand?
Entity Reconciliation is the process by which Google confirms that all mentions of a specific entity—such as your brand, your product, or your author—across the web are referencing the same thing.
- Importance: This is crucial for solidifying E-E-A-T. If Google sees dozens of sites linking to your author, it needs to be confident that “Kamran Asghar” on your site is the same “Kamran Asghar” on LinkedIn, YouTube, and an industry white paper.
- Action: You reconcile your entities by using
OrganizationandPersonSchema that includes thesameAsproperty, linking to all verified external profiles. This provides the AI with clear, explicit data to build a strong Knowledge Panel and increase your authoritative presence.
4. How can I ensure my content is chosen as a citation for an AI Overview (SGE)?
AI Overviews are highly selective and prioritize trustworthiness, clarity, and summarizability. To be cited, your content must be structured perfectly for machine consumption:
- Direct Answer Formatting: Start key sections with bolded, 1–2 sentence direct answers to the H2/H3 question.
- Use Definitive Language: Avoid ambiguity, qualifiers, and long introductory paragraphs. The AI favors concise, factual lists, and bullet points.
- Validate with External Links: Ensure any facts, statistics, or complex claims are immediately followed by an authoritative external link. This makes your content a safer, higher E-E-A-T source for the AI to reference.
5. What are the dangers of Entity Stuffing?
Just as keyword stuffing was penalized, Entity Stuffing—the unnatural, excessive repetition of entity names can signal low-quality, machine-focused content to Google.
- Google’s Preference: Modern algorithms prioritize Natural Language Processing (NLP). The system wants to see the entity used naturally within diverse, contextually relevant sentences, supported by related semantic terms.
- Best Practice: Focus on Topical Depth and Contextual Relevance. If you cover the topic thoroughly and naturally, the entity will appear the appropriate number of times, and the variety of related terms will prove your content is comprehensive, not manipulative.

